
Interprofessional and Interdisciplinary Education and Practice
The College of Health and Behavioral Studies has a long-standing commitment and a strategic goal to using interprofessional and interdisciplinary educational methods to prepare our students to collaborate with colleagues from other disciplines and professions to solve complex problems and/or to maximize outcomes in health and well-being in varied settings.
Through collaborative IPE (interprofessional education) and IDE (interdisciplinary education), we strive to enhance the quality of our learning experiences to challenge historical frameworks and current systems of oppression and injustice to improve the health of individuals and communities regardless of race, ethnicity, class, ability, age, culture, nationality, sexual orientation, SES, religious beliefs, social identities and diverse perspectives and lived experiences.
At CHBS, we recognize that IPE and IDE have important distinctions in their origin, purpose, and desired outcome. Some of these distinctions are delineated below.
|
|
Interprofessional |
Interdisciplinary |
|
Origin |
Interprofessional education and practice emerged in the past three decades. However, in the past 15 years, representatives from various health professions have convened to identify core competencies for professional practice that can be linked to accreditation standards. (IPEC, 2016) |
Many trace the beginnings of interdisciplinary studies to the Enlightenment period which emphasized reason, empiricism, and the pursuit of knowledge and truth. Over time, this pursuit of truth led to the division of knowledge development into distinct disciplines. |
|
Purpose |
To improve outcomes in health and well-being for individuals, families, and communities. |
To pursue knowledge and truth. |
|
Profession versus Discipline |
Profession: An occupation that requires specialized education, training or skills that are typically subject to regulatory and accrediting bodies that ensure education and practice adhere to an agreed upon set of standards. |
Discipline: A body of scientific knowledge that is ever-changing with the integration of creative conceptualizations and formal research findings.1 |
|
Processes |
Interprofessional: A process of interprofessional collaboration that draws upon and integrates fragmented professional perspectives to be a “means by which professionals can practice in a more collaborative or integrated fashion” **2 and thereby improve individual and systemic outcomes in health and well-being. |
Interdisciplinary: A process of answering a question, solving a problem, or addressing a topic that is too broad or complex to be dealt with adequately by a single discipline or profession… [It] draws on disciplinary perspectives and integrates their insights through construction of a more comprehensive perspective (Klein and Newell, 1998, 393-394). Interdisciplinary collaboration may also result in the creation of new disciplinary areas of study. |
While interprofessional and interdisciplinary education are distinct, they also share many things in common. Smith and Clouder (2010) summarize their commonalities as including “collaboration, boundary crossing, adopting multiple perspectives, and working with others to achieve optimal outcomes” (p. 1). McMurtry (2013) observes that interprofessional and interdisciplinary approaches share the following features: diverse perspectives, constructing common ground, negotiating conflicts, and synthesizing ideas to create something greater than the sum of its parts.
At CHBS, we conceptualize the relationship between interdisciplinary and interprofessional education as being in concentric circles, with interdisciplinary holding a wider space, whose purpose may include improving health and well-being, but may be extended to solving complex problems, discovering new fields of study, and not necessarily being bound by explicit attention to competency achievement through educational approaches.
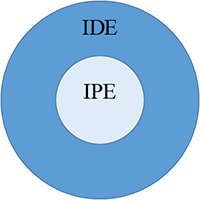
Figure 1 shows the relationship between Interdisciplinary and interprofessional education as a set of concentric circles. IDE represents a long-standing approach to education whose purpose is to pursue knowledge and truth. IPE is a subset of interdisciplinary education that is linked to outcomes in the health and human service professional fields. Successful collaboration is tied to achievement of IPE competencies as reflected in accreditation standards across a number of professional health care organizations.
The CHBS IPE/IDE Initiative welcomes both interdisciplinary and interprofessional proposals to provide educational experiences that prepare students for work settings where they are tackling complex problems through research and practice in interdisciplinary and interprofessional teams.
References:
1 Parse, RR (2015). Interdisciplinary and interprofessional: What are the differences, Nursing Science Quarterly, Vol 28(1) 5-6.
2 D’amour, D. and Oandasan, I. (2005) Interprofessionality as the field of interprofessional practice and interprofessional education: An emerging concept. Journal of Interprofessional Care, 19, 8-20. doi:10.1080/13561820500081604, p.
Smith, S., & Clouder, L. D. (2010). Interprofessional and interdisciplinary learning: an exploration of similarities and differences. In A. Bromage, L. Clouder, J. Thistlethwaite, & F. Gordon (Eds.), Interprofessional E-Learning and Collaborative Work: Practices and Technologies (pp. 1-13). IGI Global. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-61520-889-0.ch001

